| [1] Novotny NM, Ray R, Markel TA, et al. Stem cell therapy in myocardial repair and remodeling. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207: 423-434.
[2] Ohnishi S, Nagaya N. Prepare cells to repair the heart: mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of heart failure. Am J Nephrol. 2007;27:301-307.
[3] Caplan AI. Why are MSCs therapeutic? New data: new insight. J Pathol. 2009;217:318-324.
[4] Passier R, van Laake LW, Mummery CL. Stem-cell-based therapy and lessons from the heart. Nature. 2008;453:322- 329.
[5] Segers VF, Lee RT. Stem-cell therapy for cardiac disease. Nature.2008;451: 937-942.
[6] Gnecchi M, Zhang Z, Ni A, et al. Paracrine mechanisms in adult stem cell signaling and therapy. Circ Res. 2008;103(11): 1204-1219.
[7] Trachtenberg B, Velazquez DL, Williams AR, et al. Rationale and design of the Transendocardial Injection of Autologous Human Cells (bone marrow or mesenchymal) in Chronic Ischemic Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Heart Failure Secondary to Myocardial Infarction (TAC-HFT) trial: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy. Am Heart J. 2011;161:487-493.
[8] Chen S, Liu Z, Tian N, et al. Intracoronary transplantation of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for ischemic cardiomyopathy due to isolated chronic occluded left anterior descending artery. J Invasive Cardiol. 2006;18: 552-556.
[9] Crockford D, Turjman N, Allan C,et al.Thymosin beta4: structure, function, and biological properties supporting current and future clinical applications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1194:179-189.
[10] Banerjee I, Zhang J, Moore-Morris T,et al. Thymosin beta 4 is dispensable for murine cardiac development and function. Circ Res. 2012;110:456-464.
[11] Smart N, Dubé KN, Riley PR. Identification of Thymosin β4 as an effector of Hand1-mediated vascular development. Nat Commun. 2010;1:46.
[12] Shrivastava S, Srivastava D, Olson EN,et al.Thymosin beta4 and cardiac repair. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1194:87-96.
[13] Dube KN, Bollini S, Smart N, et al. Thymosin β4 Protein Therapy for Cardiac Repair. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18:799-806.
[14] Peng H, Carretero OA, Liao TD, et al. Role of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline in the antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor captopril in hypertension. Hypertension. 2007;49:695-703.
[15] Bock-Marquette I, Saxena A, White MD, et al. Thymosin beta4 activates integrin-linked kinase and promotes cardiac cell migration, survival and cardiac repair. Nature. 2004;432: 466-472.
[16] Rossdeutsch A, Smart N,Riley PR. Thymosin beta4 and Ac-SDKP: Tools to mend a broken heart. J Mol Med. 2008; 86:29-35.
[17] Smart N, Risebro CA, Melville AA, et al. Thymosin beta4 induces adult epicardial progenitor mobilization and neovascularization. Nature. 2007;445:177-182.
[18] Hinkel R, El-Aouni C, Olson T, et al. Thymosin beta4 is an essential paracrine factor of embryonic endothelial progenitor cell-mediated cardioprotection. Circulation. 2008;117: 2232-2240.
[19] Martinou JC, Youle RJ. Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell. 2011; 21:92-101. |
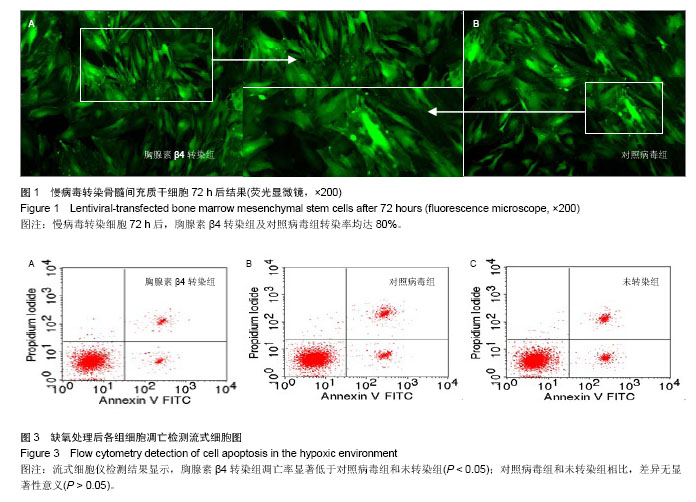
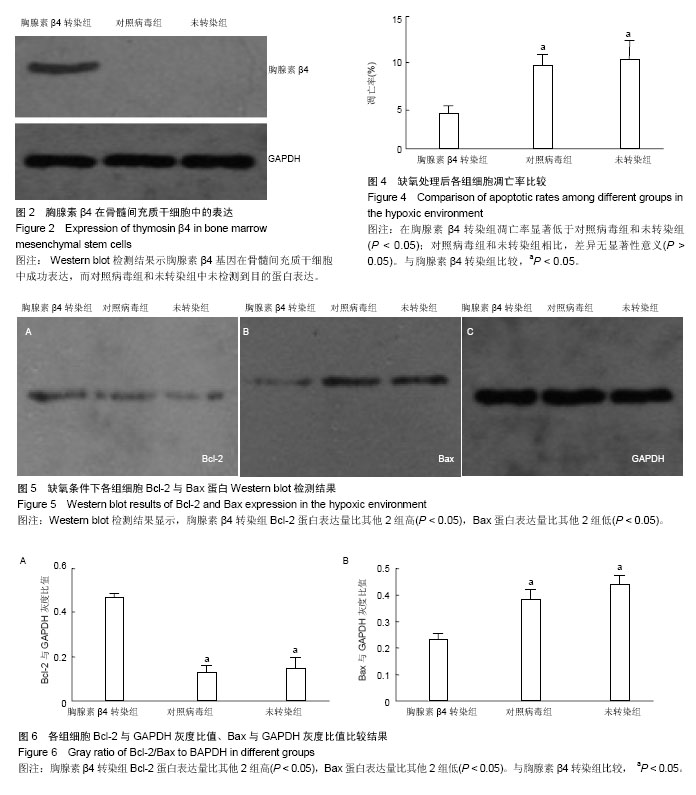
.jpg)